Last Updated on December 27, 2025
You need a clear map for handling digital assets on your balance sheet. This introduction lays out the core ideas so you can set policy, pick custody and wallet tiers, and run daily operations that stand up to audit and regulators.
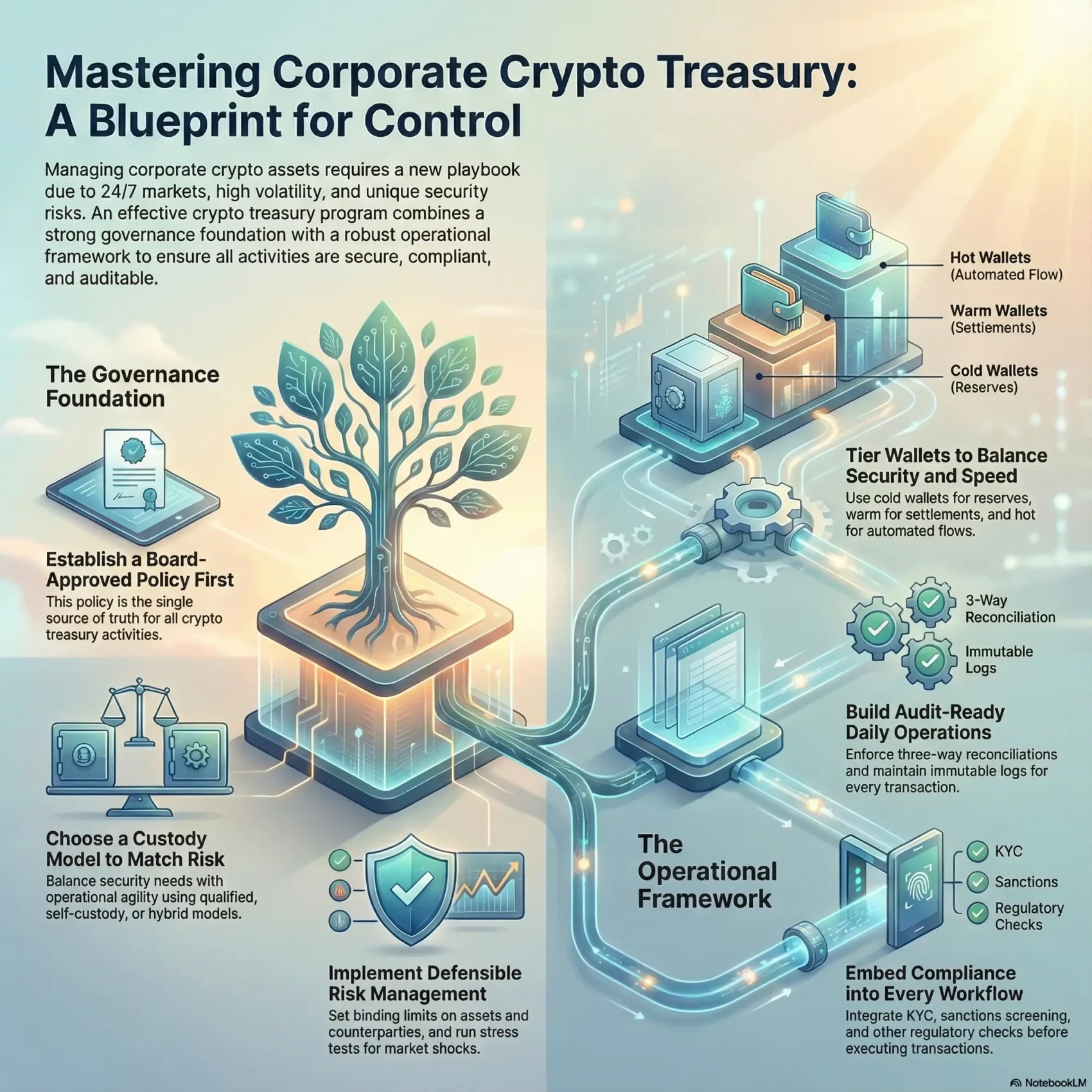
Effective programs combine governance, custody architecture, and well-documented operations. They tie approvals, limits, and immutable logs into a defensible control environment for accounting and reporting.
For corporates, asset managers, fintechs, DAOs, and nonprofits, objectives vary from vendor payments to holding reserves. You will learn how to stage cold, warm, and hot wallets, balance security with speed, and keep evidence for audits.
Standards matter: follow NIST lifecycles, FIPS cryptographic expectations, and ISO/IEC 27001 controls while aligning reporting to U.S. GAAP fair value rules.
Key Takeaways
- Get a practical roadmap from policy to pilot to scale.
- Link governance, approvals, and logs into one control environment.
- Stage wallets to balance security and operational speed.
- Keep audit-ready records for accounting and reporting.
- Align controls to standards like NIST, FIPS, and ISO/IEC 27001.
Why Crypto Treasury Management Matters Right Now
Markets that trade nonstop force you to redesign monitoring and decision flows around the clock. That reality reshapes controls, staffing, and technology for any firm holding digital assets.
24/7 markets and faster decision cycles
You face venues open every hour of the year, so continuous monitoring and pre-set limits are essential.
Design on-call paths and escalation playbooks so approvals happen in minutes, not days.
Security shifts: not your keys, not your coins
Security now rests with your controls — lost keys are a company problem, not an insurer’s.
Build signer independence, recovery plans, and tested drills to reduce operational risks.
Volatility, liquidity gaps, and technology readiness
Daily moves of 10–20% are routine for major tokens; smaller markets swing more. Calibrate position sizing and buffers to survive multi-sigma events.
Liquidity can vanish in stress, so keep liquid reserves and multiple withdrawal routes to meet obligations.
Regulation written in real time
Rules evolve across jurisdictions. Document your interpretations, geofence where needed, and prepare contingency steps for sudden regulatory shifts.
- Keep playbooks current and coordinate tightly with IT and legal.
- Adopt continuous alerts that track balances, approvals, and exposures across wallets and venues.
- Review assumptions quarterly as market structure and platform behavior change fast.
How Crypto Treasury Differs from Traditional Treasury
Corporate cash teams must rewire playbooks when digital asset markets never sleep. You move from a world of business-hour batch settlements to continuous venues that settle in minutes.
24/7 markets and faster decision cycles
You’ll pre-authorize windows and set automatic limit increases so approvals need not wait for the next banking day. Finality can be minutes, so reconciliations and exception handling must be near real time.
Security shifts: not your keys, not your coins
Unlike traditional financial setups that lean on FDIC or SIPC protections, you must design signer independence, recovery paths, and immutable logs. Use allowlists, small test sends, and dual controls to avoid irreversible mistakes.
Volatility, liquidity gaps, and regulation
Higher intraday swings and thin liquidity require bigger buffers and venue diversification. Regulation is still evolving, so document your interpretations by jurisdiction and keep policies live. Pair finance and engineering daily to manage APIs, upgrades, and new operational risks.
- Practical tip: Run frequent tabletop drills and update policy more often than in a traditional treasury team.
Scope and Core Concepts You’ll Use Every Day
Define the boundaries first. Clear scope tells your team which systems, wallets, and reports matter each day. That makes operations repeatable and audit-ready.

From custody and wallets to accounting, tax, and audit
Map your custody architecture and wallet tiers. Use hot, warm, and cold patterns so speed and safeguards match use cases.
Document approvals, limits, and evidence trails up front. Tie sub-ledgers and fair-value entries to on-chain confirmations and independent reports.
Use cases: operating flows, reserves, and product enablement
Segment flows: routine payments with small working balances, strategic reserves in BTC/ETH, and product features where allowed.
Set different oversight and limits for each use case so you manage liquidity and settlement risk predictably.
Key terms you need
Learn qualified custody versus self-custody, multisig versus MPC, and stablecoin governance expectations. These terms align legal, ops, and finance teams.
- Define custody, wallets, on/off-ramps, approvals, and evidence.
- Map use cases and assign limits and oversight.
- Align tech and controls to NIST SP 800-57, FIPS 140-3, ISO/IEC 27001, and SOC reports.
Start with Policy: Your Foundation for Control
Start policy work by getting the board to approve what you may hold, where you can transact, and who can sign off. This document becomes the single source of truth for limits, wallet tiers, approved venues, and prohibited activities.
Board-approved rules and approvals
Draft a concise board-approved policy that lists permitted assets, wallet tiers, approvers, and explicit prohibitions. Require dual control and step-up approvals for higher-risk moves so no single person holds concentrated authority.
Segregation of duties and least privilege
Apply segregation of duties: the requester, approver, and signer must be distinct roles. Use least-privilege access and temporary elevation for exceptions.
Change management and immutable logs
Document who can alter limits, signer rosters, or wallet routing. Record every change in immutable logs that map actions to human identities. Tie these descriptions to SOC-style reporting and COSO principles so external auditors can evaluate design and operating effectiveness.
- Policy matrix: assign spend limits by wallet, role, asset, counterparty, and time window.
- Pre-trade checks: enforce exposure, sanctions screening, and balance checks before execution.
- Approval matrix: thresholds plus velocity caps for added scrutiny on large or rapid flows.
- Ongoing governance: periodic attestations and scheduled reviews keep the policy current.
Safekeeping Architecture: Custody, Wallets, and Keys
Design your safekeeping stack so it matches legal limits, operational needs, and your worst-case threat model.
Qualified custody centralizes safekeeping with a regulated provider that offers segregation, SOC reports, and audit artifacts. You can place vault-tier reserves there and tie approvals and reporting to their APIs.
Self-custody shifts key generation, rotation, and recovery to your team. Align processes to NIST SP 800-57 and ISO/IEC 27001, and prefer FIPS 140-3 validated modules for cryptographic operations where possible.
Hybrid approaches and operational mapping
Many institutions blend both: a custodian for long-term reserves and a tightly controlled warm tier for routine flows. Map each wallet to its custody model and enforce policy-driven approvals.
Signer independence, recovery, and drills
Enforce signer independence across devices, teams, and jurisdictions to remove single points of failure. Design recovery with distributed backups, threshold schemes, and documented restore tests.
“Drill recovery regularly and record improvements after each exercise.”
- Request SOC reports, segregation attestations, and incident history from custodians.
- Document shared responsibilities so gaps are visible and managed.
- Keep encrypted backups under distinct administrative domains to avoid correlated failures.
Validate that your safekeeping architecture supports audit needs with confirmations and strong evidence of completeness and accuracy.
Wallet Tiering That Matches Risk and Use Case
Map where funds live and why — that clarity keeps operations auditable and resilient. A simple tier model helps you match security, speed, and policy for day-to-day activity and long-term reserves.
Cold vaults for reserves and multi-person ceremonies
Cold vaults are offline and highly restricted. Use FIPS 140-3 cryptographic modules and multi-person ceremonies for key access.
Define checklists, offline devices, and step-by-step procedures. Test access with non-value drills so ceremonies work when you need them.
Warm wallets for routine settlements with controls
Warm wallets are network-reachable but policy-controlled. Require quorum approvals, allowlists, timelocks, and daily caps for settlements.
Always run small test transactions before large moves. Capture approvals and reconcile each transfer to the sub-ledger.
Hot wallets with strict limits and continuous monitoring
Hot wallets support automated flows and low-friction operations. Constrain them with velocity caps, strict limits, and 24/7 monitoring.
Separate signing and operations environments, avoid shared devices, and document criteria for moving funds between tiers.
- Document approval thresholds and reconciliation steps.
- Configure alerts for policy violations and unusual destinations.
- Keep immutable baselines and change logs for each tier.
- Include business continuity steps for device or provider outages.
“Keep tests, checklists, and clear roles so your holdings stay secure and auditable.”
MPC vs Multisig: Choosing the Right Control Pattern
Your control pattern decision shapes who signs, what shows up on-chain, and how you restore access under stress.
On-chain policy transparency vs cross-chain coverage
Multisig enforces policy at the protocol level. That makes approvals and thresholds visible on supported chains. It is simple to audit when the chain and tooling cooperate.
MPC splits key material and produces signatures without reconstructing a private key. That yields broader platform and chain coverage depending on implementation.
Auditor expectations and recovery considerations
Auditors want evidence: who approved, how signatures were produced, and how you recover shares. Testable recovery plans matter as much as the tech choice.
- Compare on-chain transparency to off-chain policy enforcement.
- Document approvals, logs, and ceremony steps for auditors.
- Test failover paths and simulate signer loss regularly.
- Evaluate vendor support, upgrade cadence, and incident transparency.
- Include a tailored risk assessment that explains your pick.
“Neither pattern is universally superior — evidence, drills, and fit to your risks decide.”
Pick the model that aligns with your assets, venues, and audit needs, and then prove it with drills and clear logs.
crypto treasury management
Start by naming the specific functions you need—payments, reserves, or product rails—and let those objectives drive design.
Objectives, operating models, and team capabilities
You’ll clarify why you hold digital assets and align controls to each objective. Working capital, strategic reserves, and customer features demand different limits, reports, and evidence.
Choose an operating model that matches board mandate and risk appetite: qualified custody, hybrid, or self‑custody. Many firms use ISO/IEC 27001 and SOC exams to show control design and operation.
Balancing liquidity, security, and speed
Map flows to hot, warm, and cold tiers and enforce approval thresholds. Set measurable service levels for settlement time, reconciliation windows, and evidence turnaround.
Build dashboards for exposures, limits, exceptions, and incidents. Train approvers and operators so they can act under pressure. Add exception handling that pauses risky transfers and triggers extra review.
“Document what you centralize and what you run in-house, then explain that choice in a concise risk memo.”
- Define team capabilities across finance, security, and engineering.
- Measure service levels and close capability gaps with continuous improvement.
- Document controls and test them with drills so evidence meets auditor expectations.
Payments, Liquidity, and Settlement Operations
Operational payments and clear settlement steps keep daily flows predictable and auditable.
Define operating balances by wallet and currency. For stablecoin working capital, set cutoff times, fee policies, and memo standards so every transfer ties back to an invoice or business ID.
Stablecoin working capital and reconciliation hygiene
Size working capital in stablecoins and native assets to match expected outflows and settlement lag. Standardize memos and fee treatment so accounting can reconcile costs to each transaction.
Request-to-settle workflows and pre-trade checks
Build a request-to-settle flow that enforces pre-trade checks: exposure limits, sanctions screening, and available balances. Capture venue selection, approvals, and post-trade reconciliation evidence.
On/off-ramps, banking interfaces, and automated sweeps
Diversify on/off-ramp partners and document withdrawal paths, timelines, and fees. Automate sweeps from hot wallets back to custody to keep operational balances low and policy-compliant.
Three-way reconciliations and audit-ready artifacts
Reconcile on-chain data, custodian or exchange statements, and internal books on a strict schedule. Preserve artifacts—address mappings, TXIDs, approvals, and reconciliations—for auditors.
“Measure settlement timeliness, exception rates, and reconciliation breaks, then log causes and fixes to improve over time.”
- Use dashboards and tools to track daily flows and pending transactions across venues.
- Define who can approve urgent payments and how exceptions are reviewed later.
- Standardize fee handling so reporting and accounting record costs accurately.
Execution Quality and Venue Routing
A disciplined request-to-settle workflow helps you choose where and how to send orders so execution stays predictable during normal and stressed conditions.
Diversifying counterparties and withdrawal paths
Onboard multiple venues—exchanges, OTC desks, and custodial trading platforms—so you can route based on liquidity and reliability.
Document withdrawal paths, test them often, and keep fallbacks ready if a provider delays or halts outbound flows.
Fragmentation and stress widen cross-venue gaps, so log assumptions and data sources for every routing rule.
Measuring effective spread and implementation shortfall
Track effective spread and implementation shortfall to quantify slippage and routing performance.
Size orders, use time slicing, and negotiate fee tiers so routing reflects total cost, not just displayed price.
- Monitor venue health—uptime, incidents, and queue backlogs—and throttle exposure when signals degrade.
- Standardize post-trade checks so filled quantities, prices, and fees match expectations.
- Keep allowlists current and validate test withdrawals after any change.
- Enforce concentration caps across venues and counterparties to reduce correlated risks.
“Metrics describe past performance; they do not guarantee future outcomes. Log your data and be transparent about limits.”
For a practical guide to routing and business flows, see defi business transactions.
Risk Management You Can Defend
Make limits that bind: asset caps, counterparty ceilings, and wallet concentration thresholds that stop one failure from cascading.
Market, liquidity, and concentration limits
Set exposure limits by asset, venue, and partner so you never overconcentrate in one place.
Define numeric caps for positions on each chain and for each counterparty. Link those caps to automatic blocks or alerts.
- Hard caps per asset and per wallet.
- Venue and counterparty ceilings to reduce single-point failure.
- Regular reviews to adjust buffers as markets shift.
Stress scenarios: price gaps, outages, delays
Run scenario tests for sharp price gaps, liquidity evaporation, and delayed withdrawals.
Document playbooks that list de-risking steps and who has authority to act.
- Simulate slippage and withdrawal delays and record outcomes.
- Plan staged responses: hedge, pause flows, or move to backup venues.
- Map scenario results to your risk register so the board sees residual risks.
Operational hardening: allowlists, timelocks, velocity limits
Harden operations with least privilege, dual control, and signer independence across teams and locations.
- Use allowlists, timelocks, and velocity limits to stop rushed mistakes.
- Protect ceremony devices: remove radios, restrict software, and use tamper-evident procedures.
- Instrument alerts for policy violations, destination changes, or odd timing.
Keep a break-glass process that still requires multiple approvers and produces auditable evidence. Align your documentation to SOC and ISO frameworks so your risk narrative stands up to external review. Apply these controls to your crypto and treasury stacks so day-to-day operations remain defensible.
Compliance Guardrails for U.S. Organizations
U.S. organizations must build compliance lines that stop unlawful transfers before they leave your systems. These guardrails combine identity checks, screening, and clear recordkeeping so you can prove why a transfer happened.
KYC/KYB, sanctions screening, and Travel Rule processes
Verify counterparties early. You’ll run KYC and KYB, capture timestamps, and store immutable proof for each check.
Sanctions and AML screening sit in the pre-trade gate. Block or escalate matches before execution and log every decision.
OFAC expectations, geofencing, and recordkeeping
Follow OFAC by screening flows, enforcing geofences, and keeping searchable records. Retain Travel Rule exchanges and screening evidence on an auditable retention schedule.
Documenting regulatory interpretations by jurisdiction
Keep a jurisdictional matrix with citations and counsel notes. Update it on a cadence tied to rule changes and brief legal and audit teams on evidence standards.
- Test screening and Travel Rule integrations with dry runs.
- Train staff on red flags and escalation paths.
- Preserve artifacts in immutable storage and define retention timelines.
“Design controls so every originator and beneficiary exchange is measurable and retrievable.”
Accounting, Audit, and Reporting Essentials
Accounting and close routines turn on tidy records and fast tie-outs that auditors can test the day after month-end. You must document policies, valuation choices, and evidence so reporting is clear and defensible.
US GAAP: FASB ASU 2023-08 and fair value
Under ASU 2023-08, certain holdings require fair value measurement with changes flowing to net income. Disclose pricing sources, as-of times, and valuation controls each period.
IFRS classification and differences
IFRS often treats tokens as intangible assets unless held for sale in the ordinary course. If you report under both frameworks, document differences in classification and the impact on value and expense recognition.
Sub-ledgers, cost basis, and tie-outs
Run a sub-ledger with lot-level records: acquisition date, cost basis, fees, and disposition method. Map every transaction to approvals, addresses, and TXIDs.
- Reconcile custodian statements to on-chain data and the GL.
- Log breaks, root causes, and remediation steps.
- Standardize close checklists for completeness.
Independent confirmations and auditor evidence
Obtain third-party confirmations, keep SOC reports, and secure bridge letters when available. Maintain an address registry tied to business purpose and counterparty for audit trails.
“Prepare concise packs for management and the board that show balances, exposures, exceptions, and audit readiness.”
Third-Party Risk and Assurance
You should turn vendor promises into verifiable evidence and repeatable checks. That begins with independent attestations and a clear lifecycle for every provider you rely on.
SOC/ISO evidence, uptime history, and incident transparency
Require SOC reports and ISO/IEC 27001 certification as baseline proof of controls.
Review uptime SLAs, incident postmortems, and breach notification terms to judge operational maturity.
Verify encryption standards, backup handling, and how key material and other critical assets are retained or destroyed.
Lifecycle management: onboarding, refresh, termination
- Formal onboarding checklists: legal terms, service scope, and security responsibilities.
- Periodic refreshes with new evidence, SLA updates, and control deviation reviews.
- Termination playbooks for data export, key rotation/destruction, and credential revocation.
- Score vendors on transparency and resilience, limit exposure where thresholds fail.
“Keep third-party evidence tied to your audit and board reporting so oversight is continuous and verifiable.”
Incident Response and Business Continuity
A firm incident plan ties alerts to actions so operators avoid guesswork in high-pressure outages. You should pre-define playbooks for suspected key compromise, lost signer, failed withdrawal, sanctions hit, and venue outage. Each playbook must name decision makers, escalation paths, and timing expectations.
Playbooks for key compromise, venue outages, and sanctions
Pre-stage steps for immediate containment and evidence capture. Define safe halt conditions that pause transfers and raise review levels until you clear the risk.
Assign an incident commander and alternates with authority to enact recovery and notify leadership. Pre-stage recovery materials—backups, signer replacements, and alternative venues—and validate access on a schedule.
Out-of-band communications and NIST-aligned drills
Maintain out-of-band contacts so coordination continues if normal channels are compromised. Integrate monitoring alerts into incident workflows so signals route immediately to on-call responders.
Practice NIST-aligned tabletop drills that cover technical, operational, and compliance scenarios. Document lessons learned and update procedures after each exercise.
- Build clear triggers, decision rights, and response timelines.
- Test sanctions-hit processes, blocklists, and geofencing.
- Align vendor continuity plans and verify recovery contacts.
“Prepare, practice, and record the work so your team can act fast and explain every step to auditors and leadership.”
Your Technology Stack: Security and Operations
Your tech choices turn policy into practice. Start by mapping how keys, hardware modules, monitoring, and APIs connect. That map makes design, testing, and audits repeatable.
NIST key lifecycles, FIPS modules, and ISO/IEC 27001
Align key handling to recognized lifecycles. Architect generation, rotation, storage, and retirement per NIST SP 800-57 so key risks shrink from day one.
Select HSMs and libraries that meet FIPS 140-3 where feasible. Those modules raise cryptographic assurance for sensitive operations.
Run the program inside an ISO/IEC 27001 ISMS to keep policies, risk registers, and continuous improvement formal and auditable.
Monitoring 24/7 markets and disciplined change control
Deploy dashboards and alerts that track balances, limits, exceptions, and market signals across wallets and venues around the clock.
Enforce change management with approvals, testing, rollback plans, and immutable logs for any platform or wallet update.
- Segment environments and identities so admin access is limited and auditable end to end.
- Automate evidence capture—approvals, TXIDs, reconciliations—to cut manual errors and speed audits.
- Standardize API integrations for venues and custodians, handling rate limits and error conditions gracefully.
- Build shared dashboards for engineering and finance so both teams see the same truth on status and exceptions.
- Schedule resilience tests to prove monitoring and controls work after platform or policy changes.
“Design platforms so controls, observability, and recovery are part of every release.”
A Pragmatic Roadmap to Implement Crypto Treasury
Start with a clear, board‑approved plan that spells out what you will hold, why, and who can act. This keeps legal, finance, and security aligned before any funds move.
Policy first, then architecture selection
Phase 1: draft policy with counsel covering objectives, allowed assets, venues, wallet tiers, approvals, limits, counterparty onboarding, and Travel Rule flows.
Phase 2: pick an architecture—qualified custody, self‑custody, or hybrid—and decide MPC versus multisig, signer independence, and backups aligned to standards.
Pilot low‑risk flows, scale with controls, test and improve
Phase 3: pilot small balances to prove the approve→sign→settle→reconcile→report loop and measure execution quality and timelines.
Phase 4: scale only when controls pass and reconciliations are reliable; add automation and SOC/ISO attestations to support scale.
Phase 5: run recovery drills, vendor failovers, and tabletops. Codify lessons into updated procedures, training, and configuration baselines.
“Formalize policy before touching funds and tie limit increases to control evidence and audit readiness.”
- You’ll formalize a board-approved policy before touching funds.
- You’ll pilot low-risk flows and measure execution and settlement timelines.
- You’ll build a capability roadmap for people, processes, tools, and governance.
Conclusion
Conclusion
crypto treasury management succeeds when governance, custody architecture, and daily operations form a single, auditable loop.
Turn policy into practice with clear owners, scheduled tests, and immutable logs. That lets your treasury management program protect assets and produce evidence for auditors and boards.
Maintain adaptable controls as the market shifts. Diversify venues, run stress drills, and keep reconciliation tight so settlement and liquidity risks stay visible.
Use a phased roadmap: pilot low-risk flows, scale with controls, and document every decision. These practices help your company keep managing crypto responsibly and convert strong controls into lasting advantage.