Last Updated on December 31, 2025
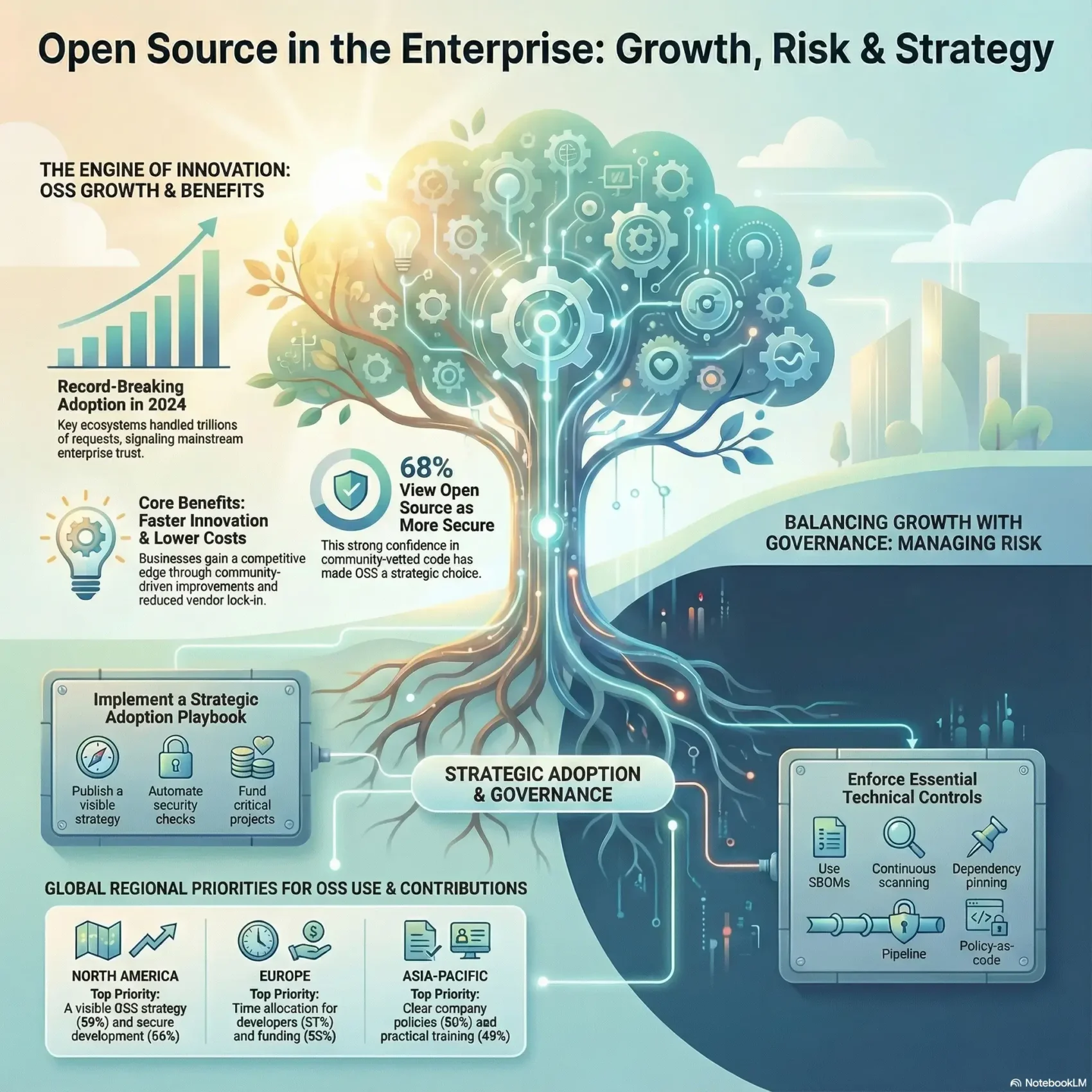
You are navigating a world where community-built code powers more of your stack than ever. In 2024, ecosystems hit record consumption: npm saw about 4.5 trillion requests, PyPI neared 530 billion, and Maven Central logged 1.5 trillion. These numbers show real momentum and signal mainstream trust.
The latest report also shows confidence in security: 68% of respondents view open source software as more secure than proprietary options. That shift helps your teams move faster, lower costs, and tap a global community that improves the tools you use.
Across cloud, data, and AI work, companies and organizations now standardize on community-driven projects to speed delivery and boost innovation. This section maps the state of the market and gives practical context so you can act with clarity today.
Key Takeaways
- Record usage in 2024 proves community software is operationally mature.
- Community projects drive faster innovation and lower total costs.
- Security confidence is rising; many view OSS as more secure than closed alternatives.
- Standardizing on community code helps teams scale and choose richer technologies.
- Balance growth with governance to keep momentum and avoid rework.
- This guide will show practical steps to operationalize community-driven software in your environment.
The state of open source in the past few years: where you are today and how you got here
The shock of 2020 rewired how teams relied on community-built code and cloud infrastructure. As remote work scaled, you needed resilient systems fast. That year pushed organizations toward automation, orchestration, and service mesh to stabilize delivery.
Early moves weren’t experiments for long. By 2024, usage data and reports show community components moved into production across CI/CD, data platforms, and AI frameworks. You now treat many source libraries as core building blocks rather than optional tools.
From disruption to normalization
The 2020 OpenLogic report framed the shift: higher adoption rates, clear barriers, and new priorities. Over subsequent years, teams tightened governance and layered security controls. That maturity made open source software a strategic choice.
- Growth and trust: ecosystem downloads rose and security confidence strengthened.
- Strategic shift: investment moved toward vendor-neutral technologies to reduce risk.
- Your path: year-over-year use changed from trial to production-first practices focused on reproducibility and maintainability.
Understanding this arc helps you explain past decisions to stakeholders and plan where to invest next. The state of OSS today is less about novelty and more about disciplined, value-driven use.
Open-source adoption by the numbers: growth, ecosystems, and AI-fueled demand
Your pipelines now pull from registries that handled trillions of requests last year, and that scale matters.
Explosive consumption: npm logged roughly 4.5 trillion requests in 2024 (≈70% YoY), PyPI reached about 530 billion (≈87% YoY), and Maven Central saw 1.5 trillion. NuGet added 159 billion requests. These figures benchmark your own usage and show the scale of modern software supply chains.
AI and deep dependency trees
AI and ML adoption, especially in Python, fuels rapid growth. Projects pull layered dependencies that boost innovation but increase transitive complexity.
Maintenance, versions, and noise
Maven Central averages 28+ versions per project, which translates into more patching and backport decisions for teams.
“Over 704,102 malicious packages have been identified since 2019, with 512,847 documented last year.”
- Translate data to action: instrument consumption dashboards and enforce SBOM accuracy.
- Reduce noise: curate catalogs and automate vetting to protect developer velocity.
- Limit blast radius: use policy-as-code, staged rollouts, and automated PRs to manage risks.
Regional trends in OSS: priorities and actions across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific
Where you operate matters. Your region shapes what leaders fund, which policies they enforce, and how teams learn to contribute to source projects. This snapshot helps you match investment to regional expectations and move from trial to scale.

North America: strategy, security, and automation
Security confidence runs high: 77% say the open source model leads to better security. To increase use, 59% call for a visible OSS strategy and 56% want improved secure development.
Practical moves you can model: provide automated tooling to enforce policy (51%), allocate employee time (55%), and fund projects (55%). These steps raise participation and protect delivery.
Europe: public funding, compliance, and education
Europe shows strong support for making publicly funded software available as source—82% agree. Boosting use there means adding legal and compliance support (48%) alongside secure development improvements.
To increase contributions, prioritize time allocation (57%), funding (55%), and company-wide education (52%). That mix solves both legal hurdles and cultural buy‑in.
Asia-Pacific: cautious optimism, clear rules, and training
Asia‑Pacific reports the least regulatory uncertainty (34%) and some belief that global rules will help participation (37%). Focus on clear policies (50%) and practical training (49%) to unlock contributions.
“Allocate time, fund projects, and teach your teams—those three moves amplify use and contributions.”
- Checklist: visible strategy, secure dev, automation, legal/compliance support, education, and time allocation.
- Align your compliance and support playbooks to regional norms to reduce friction and speed cloud and technologies rollouts today.
Industry perspectives: how sectors prioritize benefits and contributions
When you compare industries, the benefits and contribution patterns reveal clear, actionable priorities for your teams.
Cross-industry IT and telecom/media
IT companies cite standards and interoperability (62%) and innovation (59%) as top benefits. Telecom and media rank innovation (61%), productivity (56%), and transparency (53%).
Key techs: AI/ML, operating systems, and cloud/containers drive the most value. Contributions focus on cloud/containers, CI/CD, and web/app development.
Government, healthcare, and financial services
Public services and healthcare emphasize trust, data, and compliant systems. AI/ML and operating systems show strong usage across these sectors.
Financial services prioritize standards and interoperability (59%) and invest in CI/CD and DevOps to speed delivery and resilience.
Industrial and manufacturing
Manufacturing leans on operating systems, embedded/IoT, and cybersecurity to support edge and OT transformation.
Contributions here often target OS projects, IoT stacks, and safety-critical tooling to protect infrastructure and product lines.
- Match sector goals to where you invest — cloud and CI/CD often give the highest cross-industry impact.
- Use the report data to benchmark your company and direct developer effort to the highest-value technologies.
Security realities in community-driven software: confidence, risk, and the modern supply chain
Confidence in community code remains high, yet your team faces a widening gap between perception and exposure. The report shows 68% of respondents view open source as more secure than closed alternatives. At the same time, documented threats have surged, creating real challenges for your pipelines and cloud builds.
Perception vs. exposure
Your belief in OSS security is backed by community vetting and fast fixes. Still, the volume of malicious packages undermines that trust without better controls. Reconcile perception with evidence by tracking SBOMs, continuous scanning, and provenance checks.
Malicious package surge
Since 2019 more than 704,102 malicious packages were identified, with over 512,847 in the past year alone. npm has been a hotspot for spam and malware, and PyPI temporarily paused new releases to slow attacks.
Ecosystem hotspots and practical safeguards
Turn lessons into action: use dependency pinning, automated pull requests for updates, staged deployments, and policy-as-code. Frame risks as business issues—delivery impact, reputation, and response costs—to secure budget and support.
- Developer hygiene: pin dependencies, publish SBOMs, and scan continuously.
- Platform controls: provenance checks, automated vetting, and staged rollouts.
- Measurement: combine ecosystem report metrics with your telemetry to drive improvement.
For context on how modern stacks and edge builds change trust boundaries, see this short primer on edge computing and supply chain controls: edge computing and supply chain context.
Open-source adoption playbook: strategy, compliance, and sustainable contributions
Start by treating source programs as strategic assets that need clear ownership and measurable outcomes. Publish a visible OSS strategy that explains where you will use community code, which projects you support, and who signs off on priorities.
What you can do now
Make policy simple and automatic. Embed secure development into CI — threat modeling, SCA and SAST checks, and signed releases. Use policy-as-code so compliance is a guardrail, not a blocker.
Funding and time
Budget for maintainers or sponsored workstreams. Allocate contributor hours and create clear contributor paths: docs, tests, and triage tasks. These steps reduce single points of failure and grow durable teams.
- Governance: set licensing, deprecation, and security review rules before source hits production.
- Measurement: track reliability, MTTR, and developer satisfaction to show ROI.
- Communication: publish simple blog updates and use organization-level report data to justify training and support.
Over time, iterate your playbook with feedback from regional teams and other organizations. That approach keeps your program pragmatic, scalable, and aligned with the cloud and web technologies you rely on.
Conclusion
You’ve watched community code move from experiment to backbone. In 2024 that shift showed record-scale growth and clear benefits for teams worldwide. Use those facts and the report data to guide your plan for the next year.
Keep a simple checklist: publish a visible strategy, automate secure development guards, fund maintainers, and invest in training. These moves let you harness community strength while managing supply chain risks.
Track progress with small, regular updates — a short blog or quarterly review. With clear governance and steady participation, open source and oss can be a lasting strategic advantage for your software development today.