Last Updated on December 18, 2025
Viewing app choice as part of your digital strategy lets your team enable innovation while keeping controls in place. Automated discovery and risk classification give continuous insight into who uses which tools and how data flows.
With a clear approach, your security group becomes a partner to the business. You gain unified offboarding, zero-touch lifecycles, and consistent guardrails across teams.
The result: faster time to value for your organization and stronger, measurable security for the company.
Key Takeaways
- Treat app adoption as a business enabler, not an obstacle.
- Use automated discovery to find risky apps and map data flows.
- Make security a partner so teams can choose tools safely.
- Standardize lifecycles for onboarding, offboarding, and compliance.
- A structured approach boosts agility for startups and enterprises alike.
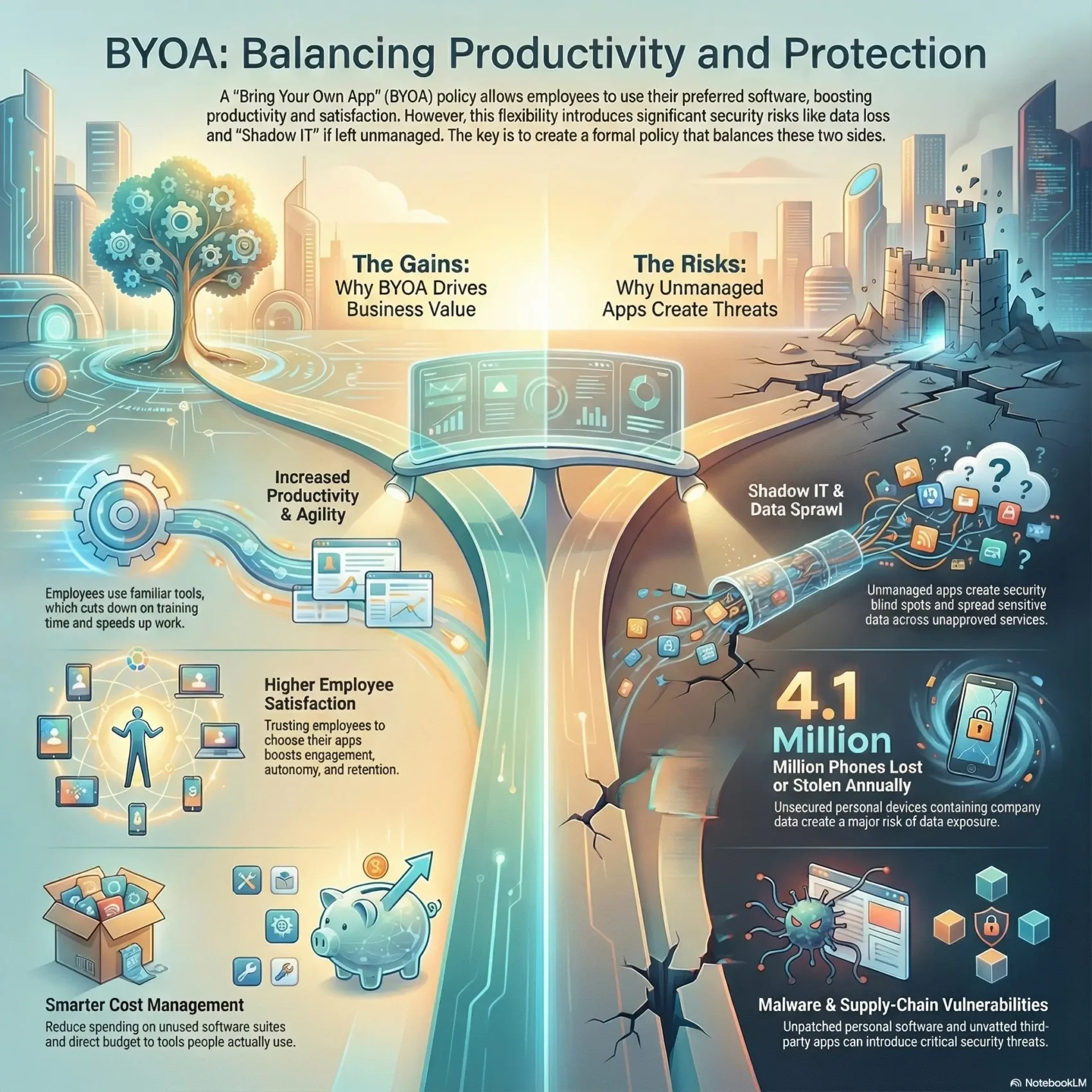
Why BYOA matters right now for your business
Hybrid schedules and widespread cloud adoption mean software choices happen outside IT. Employees already use personal tools and phones to finish tasks, so app choice is no longer an exception—it’s part of day-to-day work.
Supporting BYOD momentum makes sense. With 82% of organizations allowing personal devices, letting teams pick apps doubles down on gains you may already see in productivity. Employees learn tools faster and switch context less, reducing time to complete work.
For businesses, the benefits are practical. You lower ramp-up costs, speed experimentation with fit-for-purpose apps, and cut delays caused when standard software lags behind needs.
- Employees feel trusted and autonomous, which boosts engagement and retention.
- IT and security gain clearer visibility into real app use, so you can standardize wisely.
- Repeatable processes scale across teams and avoid slow, one-off approvals.
The takeaway: channel this reality with controls and visibility rather than resist it. Unsanctioned app use will happen if you don’t provide a safe, repeatable way for employees to use the cloud and their devices productively.
Balancing innovation and risk: what you gain—and what can go wrong
When teams pick tools on their own, you gain speed—but also new exposure points to manage. The right approach lets your company harvest innovation without sacrificing control.
Productivity, cost savings, and employee satisfaction from app choice
You’ll see measurable productivity gains when employees select the right application for a task. They cut ramp time, automate repetitive tasks, and avoid waiting on lengthy approvals.
Cost benefits follow: you reduce shelfware, limit over-licensing of large software suites, and direct budget to tools that teams actually use.
Morale improves too: employees feel trusted and more likely to stay when they can choose tools that fit their workflows. A curated catalog of trusted productivity apps makes adoption safe and fast. productivity apps
Shadow IT, data loss, and malware risks in cloud and mobile workflows
Unmanaged app use creates Shadow IT and data sprawl across cloud services. Personal devices may run unpatched or jailbroken software that opens pathways for malware.
- Lost or stolen phones (about 4.1 million yearly) raise data exposure risks.
- Accidental sharing or weak access controls can leak confidential information.
- Third-party vendors and unmanaged applications add supply-chain risk.
Seeing this as a velocity enabler for teams and security
Automated detection and classification of risky apps increase visibility without blocking work. Early awareness lets your security team apply least-privilege access and route sensitive data to approved environments.
The takeaway: you don’t have to choose between speed and safety. With clear boundaries, continuous monitoring, and fast approval paths, innovation and protection become co-drivers for your company.
Start with visibility: discover the apps your employees actually use
Start by mapping the real software people use every day so you stop guessing where risk hides. Visibility gives you a clear snapshot of who uses which application and where sensitive information lives.
Automated SaaS discovery to reduce blind spots and Shadow IT
Automated discovery finds new applications without manual surveys. It captures domains, permissions, scopes, and connection patterns across browsers and cloud services.
That reduces Shadow IT and shows which users and teams access each application. You can then route popular tools through SSO and MFA fast.
Classifying “risky apps” and mapping data flows across users and teams
Classify risk by vendor reputation, data residency, encryption, admin models, and incident history. Enrich each app entry with purpose, owner, and data categories so approvals are faster and controls fit the use case.
- Create a living catalog of observed apps and users to drive SSO, access tiers, and unified offboarding.
- Map where data moves between users, teams, and cloud services to align retention and access rules.
This visibility helps your company retire duplicate tools, prove compliance, and keep work moving without costly bottlenecks.
Your BYOA policy: the essentials to put in writing
You need a clear, written standard that lets teams choose tools while protecting critical systems. Make it short, readable, and easy to follow so people actually use it.
Scope, ownership, and acceptable use
Define scope by listing which applications and software categories are covered and what classes of data fall under controls. Clarify how personal and corporate contexts must stay separate on each device.
Assign ownership: who approves apps, who runs the catalog, and which team handles risk ratings and lifecycle management.
Data handling rules
Document classification, retention, and cloud storage boundaries for regulated information. State where sensitive data can and cannot be stored, and require encryption and logging for high-risk stores.
Access requirements
Mandate SSO where possible and MFA for high-impact applications. Use least-privilege defaults and time-bound elevation to limit exposure from users and dangling accounts.
Governance, reviews, and exceptions
Set review cadences, exception processes, and clear escalation paths. Include steps for onboarding, deprecation, and automated deprovisioning so access is revoked when roles change.
“Make the rules easy to follow so security becomes an enabler, not a blocker.”
- Require users to secure credentials and report suspicious activity.
- Keep the document accessible with links to training and quick request forms.
- Automate visibility so your security team knows which applications employees use and why.
Security-by-design: controls that make BYOA safe without slowing work
Design controls around how people actually work so your teams stay fast and your data stays protected. Start with a clear choice between app-focused and device-focused approaches and map each control to risk.
MDM vs. MAM: secure corporate data without owning personal devices
Choose MAM when you need to containerize corporate application data on personal devices. It protects work apps and files with minimal intrusion and fits common byod scenarios.
Use MDM for high-risk roles or regulated workloads that require stronger device management and posture enforcement. That gives you full device management, patching, encryption, and greater assurance.
Zero trust, VPN, and endpoint protections
Apply zero trust principles: continuous verification, least privilege, and segmentation. Tune conditional access so unusual sign-ins or unmanaged devices face step-up verification or block.
Combine MFA, SSO, per-app tunnels or SASE for sensitive traffic, and standard endpoint protections like anti-malware, OS patching, and device encryption. Harden application scopes, limit risky OAuth grants, enable DLP, and keep logging active.
The result: controls that match risk and preserve usability so your teams accept secure paths instead of avoiding them.
Compliance and legal guardrails you can’t ignore
When personal devices touch corporate information, clear legal boundaries become non-negotiable.
Documented consent, privacy boundaries, and audit readiness
Get written consent so employees know what your company can view, access, or wipe on a device. That clarity reduces disputes and supports lawful action.
Separate personal content from corporate information. Describe selective-wipe behavior and how you protect private files while securing business accounts.
- Keep approvals, risk assessments, and access reviews for audits.
- Log configuration baselines and SSO links to show controls for auditors.
- Train staff and collect signed acknowledgments to cut legal exposure.
Wipes, searches, and offboarding on personal devices—doing it lawfully
Define lawful steps for remote wipes, searches, and eDiscovery so actions are authorized and proportionate.
Address edge cases like evidence of misconduct and law enforcement seizures. Involve legal, preserve chain of custody, and protect company data during any external request.
“Clear, consent-based rules and neat audit trails turn security obligations into operational hygiene.”
Align with compliance frameworks so your enterprise can show auditors that access, protection, and revocation work day to day. This reduces risks that cause lawsuits and keeps your organization resilient.
Lifecycle management: onboarding, changes, and secure offboarding
Treat user lifecycles as a single, auditable workflow that spans HR, IT, and security. That mindset reduces manual handoffs and closes gaps where ex-employees or contractors keep unintended access.
Start with an onboarding checklist that ties app access to roles. Use SSO groups and MFA from day one so new employees can work securely without delays.
Unified offboarding and role changes
Automate change management so role moves add and remove permissions instantly. Connect HR events to identity systems to start offboarding the moment someone leaves.
- Centralize offboarding: revoke tokens, deprovision accounts, rotate shared credentials, and remove dangling users across all connected apps.
- Apply selective wipe on managed apps when a device unenrolls, removing corporate data while respecting personal privacy.
- Set time-bound access for contractors with automatic expiry to lower long-term risk and help compliance.
Close the loop: transfer ownership of shared files, audit logs during transitions, and measure cycle time so your team improves the process over time.
“Automated lifecycles turn onboarding and offboarding from a challenge into a repeatable strength.”
Enablement beats enforcement: empowering teams to choose wisely
Giving teams the right guidance lets them choose apps without slowing work. Start with practical supports that make safe choices obvious and fast.
Train employees on common software scenarios, permission management, and privacy settings. Short, role-based sessions help users spot risky links and manage access in the apps they select.
Create an approved app catalog that highlights safe-by-default options and explains why each tool fits certain use cases. Pair that catalog with templates for business need, data types, and ownership so requests are tidy and fast.
Use automated discovery to prefill reviews. A fast-track process speeds low-risk approvals while keeping security oversight where it matters.
“Enablement builds trust: teams move faster, and your company keeps control.”
- Maintain dashboards that show adoption and which users favor each application.
- Offer a simple request workflow and two-way feedback so the catalog improves over time.
- Tie outcomes to metrics—fewer escalations, faster time to value, and higher productivity.
Conclusion
Your company wins when you treat app adoption as an intentional capability that supports speed and safety.
Make visibility, classification, and strong access controls part of everyday work so employees can choose tools that fit real needs without creating blind spots in the cloud.
Use SSO, MFA, and least-privilege rules together with automated discovery and unified offboarding. These practical solutions cut approval time and reduce risks while keeping your team productive.
Commit to a steady operating rhythm: discover, assess, approve, and monitor. Track outcomes like cycle time, adoption of recommended choices, and reductions in risky behavior to prove progress.
Do this, and you protect information while empowering teams to get work done.