Last Updated on January 26, 2026
You’ll learn a clear definition of a global expansion strategy and why it matters. This guide shows a step-by-step plan to take your business into new markets with fewer surprises and stronger execution.
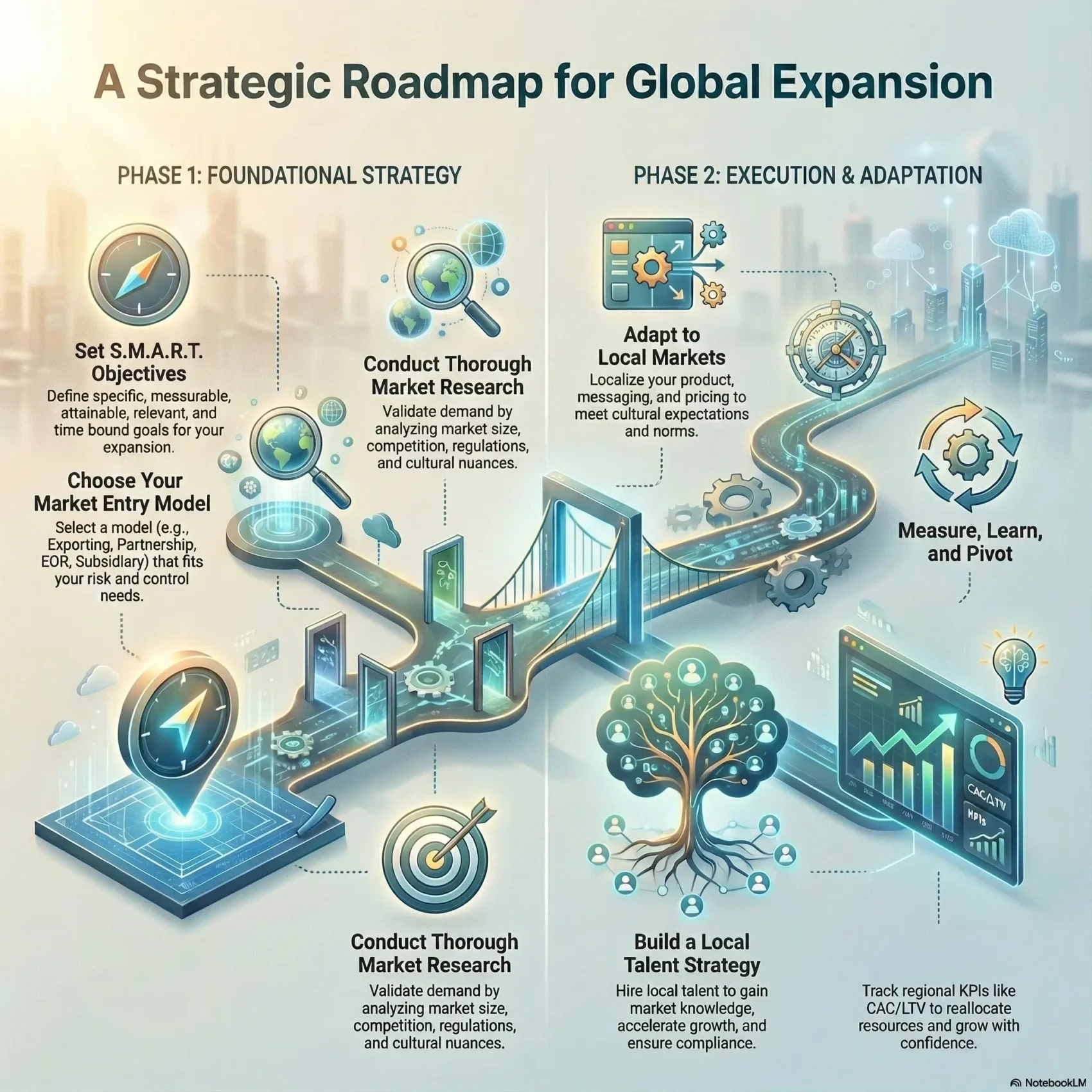
Strong plans share four core ingredients: defined objectives, deep market research, cultural adaptability, and a hiring approach that fits local needs. These elements help you align daily actions with long-term goals.
Companies expand for many reasons: to increase revenue, diversify risk, access talent, and boost brand presence. Real examples — like Walmart’s moves into Mexico and Canada versus Target’s Canada misstep — show how timing and fit matter when taking business around the world.
This introduction previews a practical framework you can use today. You’ll get checklists, market tests, and entry options so your company grows without overextending resources.
Key Takeaways
- Define clear objectives before you enter new markets.
- Base decisions on research and local adaptability.
- Avoid copying your domestic playbook abroad.
- Use examples to learn timing and market fit.
- Tie hiring, pricing, and compliance back to goals.
What a Global Expansion Strategy Really Means for Your Business
You’re not just selling more when you enter other countries. International expansion covers sales, hiring, and running operations in new places. That makes your plan bigger than a product launch.
Start by mapping the scope: first market entry, then the steps for multi-year growth. Market research and local rules shape that path. You must also adapt products, pricing, and hiring to fit each market.
- Definition: Sales, talent, and operations abroad — not only exports.
- Scope: From test entry to a durable operating system.
- Checks: Market research, regulatory review, and cultural fit.
- Business fit: Revenue goals, risk diversification, talent access, or cost advantages.
Remember: possible isn’t the same as smart. Use clear decision points for doing work in-house or partnering with local experts. Link day-to-day actions back to your objectives so you enter, operate, and learn in new markets without losing focus at home.
For practical tactics on coordinating channels and partners as you grow, see this omnichannel playbook.
Why Go Global Now: Benefits You Can Realistically Capture
When done with focus, spreading your operations can create measurable wins: more customers, better talent, and lower unit costs. You can capture early revenue from new audiences while you test product-market fit.
New revenue streams and a larger customer base
Tap additional markets to grow recurring sales and diversify where revenue comes from. Entering the right international markets may offer access to segments that mirror your best domestic customers.
Access to specialized international talent and economies of scale
Hiring abroad gives you access to niche skills—engineering, creative, and domain experts—that speed product development.
As volumes rise, you can lower per-unit costs through better procurement and distribution. This is where economies of scale turn into real margin gains.
Diversifying risk and enhancing brand recognition
Operating in several markets reduces reliance on one market and makes your company more resilient to local downturns.
Expanded presence also lifts brand recognition and credibility. Customers and partners often trust companies that show consistent performance across regions.
- Identify near-term wins tied to your business model.
- Quantify payback timelines before larger investment.
- Map partner ecosystems that compound value over time.
Global Expansion Strategy
This section gives you a concise, repeatable framework to plan, launch, and learn as you enter new markets. Use it to keep every decision tied to measurable business goals and to avoid costly guesses.
The ultimate guide framework you’ll use throughout this playbook
Start with clear objectives that match revenue, brand, talent, or risk goals. Pair those with rigorous market research to validate demand and local rules.
Aligning expansion with your existing business goals
Adapt products, go‑to‑market, HR, and support so your business operations function in each market. Build a talent plan that balances speed, cost, and quality.
“Good plans combine clear objectives, research, cultural fit, and a hiring model that scales.”
- Define governance and decision rights to move fast while protecting compliance.
- Use a sequence: objectives → research → entry model → localization → talent → tech → compliance → KPIs.
- Measure early wins and adjust to create a successful global expansion over time.
Set Clear, S.M.A.R.T. Objectives Before You Take Off
Start by turning broad ambitions into crisp, measurable goals that guide your next market moves. Clear objectives stop guesswork and keep your team aligned as you plan an expansion strategy.
Turning vague intent into measurable outcomes
Use S.M.A.R.T. goals: specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. That makes it obvious when a market test is working.
Examples for SaaS, manufacturing, and service companies
Example: a SaaS company aims for 15% of revenue from Europe within 18 months. That ties product, sales, and support targets to the new market.
Example: a manufacturer targets a 20% cost reduction by moving some production to Southeast Asia. You measure cost per unit, lead time, and quality to validate the move.
- You’ll translate ambition into S.M.A.R.T. objectives so everyone knows what success looks like when going global.
- You’ll scope what’s realistically attainable, like hiring a five-person local team before a full launch.
- You’ll set time-bound milestones (market launch by Q3) and cascade targets into KPIs for sales, product, finance, HR, and ops.
“Good objectives force tradeoffs and surface the evidence you need to choose markets and entry models.”
Build a baseline to compare markets and measure revenue streams, cost, and compliance. Use those facts, not hunches, to guide growth.
Conduct Thorough Market Research to Validate Demand
Before you spend a dollar on a launch, verify that real customers exist and will pay for your offering.
Start by sizing the market and measuring saturation. Use public reports, customer interviews, and competitor revenue estimates to see if demand covers your cost base.
Then analyze customer behavior and pricing norms. Check payment preferences—invoice terms, cards, or digital wallets—because even small differences change conversion and cash flow.
Regulation and cultural fit
Catalog local regulations early: labor, tax, and sector-specific rules can block a launch if ignored.
Evaluate cultural nuances that shape messaging, onboarding, and support. Localization isn’t just translation; it’s adapting how you sell and retain customers.
“Build an apples-to-apples data set so you can compare markets and prioritize where to invest first.”
- Size demand: estimate addressable market and realistic share.
- Map competition: identify saturation and white-space opportunities.
- Validate pricing: test willingness to pay and profitable segments.
- Check compliance: list regulatory blockers before committing resources.
When you conduct thorough market research, you pressure-test assumptions that worked at home and avoid costly fits in new markets. That practice keeps your company agile and informed as it plans growth and expansion.
Choosing Your Market Entry Model: Pros, Cons, and Fit
Your choice of entry model shapes control, cost, and the speed of market learning.
Exporting lets you test demand with low upfront cost and limited risk.
It’s fast to start but offers limited control over pricing, distribution, and brand experience.
Licensing, partnerships, and joint ventures
Licensing or franchising speeds rollout and conserves capital. It can, however, create quality and brand control risks.
Joint ventures share risk and tap local know-how. They need clear governance to avoid decision deadlocks.
When control matters: subsidiaries and acquisitions
Subsidiaries give you full control and profit capture but raise cost and compliance work.
Acquisitions deliver immediate presence and scale. They carry integration risk and often demand heavy management focus.
Test fast with an Employer of Record
An EOR helps you hire compliant staff, manage payroll and benefits, and save time without entity setup.
Start lean—exporting or EOR—and move to deeper investment only after you conduct thorough market checks.
“Choose the model that matches your risk tolerance, resources, and how much control you need.”
- You’ll compare market entry options to fit your resources and control needs.
- You’ll see when low-cost tests make sense and when full control justifies higher investment.
- You’ll outline a phased path from testing to full-market commitment.
Adapting to Local Markets Without Losing Your Core
Adapting your offer to local norms helps you win customers without diluting what makes your company strong.
Product and service localization that respects cultural norms
You’ll localize content, UX, pricing, and support so your product service fits the local market. That means more than translation; it means adjusting flows, images, and payment options to match what users expect.
For workforce decisions, note how local culture shapes benefits. For example, France’s 35-hour workweek and five weeks of paid vacation reflect deeper values. Misreading those norms harms attraction and retention.
Maintaining consistent brand standards across regions
Maintaining consistent brand standards keeps trust while you adapt messaging and imagery for each target market. Document what’s non‑negotiable and what can flex.
- You’ll tailor compensation and recognition to local motivators to speed hiring and reduce churn.
- You’ll build feedback loops with local teams so products services stay relevant as preferences evolve.
- You’ll create playbooks that protect core values and help maintain consistent customer experiences across markets.
“Aligning work norms and product choices to local expectations improves both employer brand and customer loyalty.”
Build a Sustainable Global Talent Strategy
Hiring the right people in each new market is one of the fastest ways to gain traction and reduce risk.
Contractors give flexibility and speed, but they raise misclassification risk and often weaken team cohesion. Many markets favor full-time roles with benefits.
Employer contributions can reach 50% of base pay in some countries. Ongoing market intelligence — like salary inflation in Malta’s iGaming sector — helps you budget accurately.
Compensation, motivation, and employer brand by culture
Tailor offers to local culture and expectations. In some markets, benefits and stability matter more than headline salary.
“Build offers that reflect local norms so top talent sees your company as a long-term bet.”
- You’ll choose employees where commitment and mission alignment matter most.
- You’ll factor total employment costs, not just base salary.
- You’ll hire multilingual staff and set clear communication norms to reduce language barriers.
- You’ll keep contractor flexibility but protect institutional knowledge with permanent roles.
Practical takeaway: blend short-term hires with a core local team so your business grows with lower risk and stronger in-region ownership.
Hire the Best Local Talent to Accelerate Fit and Speed
Hiring local leaders speeds your path to product-market fit and shortens sales cycles. Place a few strategic hires in the target market to gain language fluency and local context immediately.
You don’t need a full office. Start with roles that move the needle: sales reps, support agents, and project managers with deep local ties.
- Prioritize impact: hire people who open doors and close deals fast.
- Shorten cycles: local hires bring credibility that improves customer satisfaction and speeds wins.
- Optimize cost: keep travel low and let in-country staff handle day-to-day while your home team focuses on core business.
- Validate lean: hire minimal headcount to test the market before you scale, lowering risk and learning fast.
- Onboard to influence: create training that shares your culture and empowers hires to shape local tactics.
“Local hires convert relationships into momentum.”
This approach helps your company enter new markets with faster learning and measurable growth while keeping your overall expansion strategy lean and focused.
Form Strategic Local Partnerships to Reduce Time-to-Market
Forming the right local partnerships cuts weeks off your launch timeline and lowers execution risk. You’ll rely on partners to handle hiring, payments, logistics, and market outreach so your core team can focus on product and customers.
Compliance and employment partners: EOR vs. PEO
EORs enable hiring without a legal entity and handle payroll, benefits, and local HR. They help you hire compliantly and save time when entering a new market.
PEOs usually require you to have a local entity and suit companies ready for deeper commitment. Choose an EOR to test demand, then move to a PEO or entity when you scale.
HRIS, banking/FX, supply chain, and market development partners
Pick HRIS tools like Workday or BambooHR to centralize multi-country data and workflows. Add banking/FX partners such as Wise or Mercury to manage cross-border payments and currency risk.
Assemble supply chain and distribution partners to reduce last-mile friction. Engage agencies, resellers, or local agents to speed pipeline building and adapt messaging for each target market.
Due diligence: track record, financial stability, governance
Run strict checks on partner track record with similar companies, financial health, and governance. Ask for references and contract SLAs that define uptime, compliance responsibilities, and escalation paths.
- You’ll identify where an EOR helps you launch and hire compliantly without an entity.
- You’ll centralize HR with proven platforms and reduce currency friction with banking partners.
- You’ll contract distribution and market development partners to move products and services faster.
- You’ll require partner SLAs, audits, and governance reviews to reduce vendor risk.
“Choose partners who shorten your path to customers and protect you from regulatory compliance gaps.”
Technology Stack for Going Global Without the Growing Pains
The right mix of tools turns scattered teams into a coordinated, compliant machine. Pick systems that reduce manual work, keep leaders aligned, and help your company move into new markets with less friction.
ATS and global HRIS/payroll for compliant local hiring
Use an ATS like Teamtailor to streamline recruiting and a global HRIS/payroll to hire compliant local staff and save time on admin. This combo cuts onboarding delays and centralizes benefits, contracts, and taxes.
Project management and communication across time zones
Coordinate work with Trello, Monday.com, or Asana so teams avoid handoff delays. You may need clear SLAs, overlapping hours, and async docs to keep work flowing across each market.
Finance, FP&A, and equipment at scale
Tools like Brex and Carta improve forecasting, expense control, and audit readiness for companies operating in several markets. Equipment platforms like Growrk may offer global device tracking so provisioning works in 150+ countries.
- Standardize workflows but allow local flexibility to protect core business operations.
- Harden security and data privacy so product service delivery stays fast and compliant.
- Integrate systems to cut manual reconciliations and give leaders real-time, comparable metrics.
“Choose tools that let teams move quickly while you keep compliance and financial controls tight.”
This tech approach supports measured expansion and helps your business capture growth in each target market during international expansion.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management You Can’t Ignore
Compliance is a front-line business requirement, not a legal afterthought.
Each country has its own rules that affect how you hire, price, and deliver a product service. Missing one requirement can pause operations and cost far more than the filing fee.
From labor law to tax: staying compliant in each local market
You’ll map local regulations across labor, tax, privacy, and sector rules for every market you enter. Build internal controls and audit trails so you show regulatory compliance proactively, not reactively.
Real-world example: Germany’s Central Packaging Register
In Germany, manufacturers and sellers must register with the Central Packaging Register and help reduce packaging waste. Failure to register can trigger fines up to €200,000. That example shows why you must pre-check product service obligations before launch.
- Study cultural nuances embedded in labor laws so policies fit both letter and spirit.
- Decide when in-house counsel is enough and when local legal experts are required.
- Create a risk register with owners, mitigation plans, and triggers for fast action.
- Schedule periodic compliance reviews to catch regulatory updates that affect pricing, labeling, or operations.
“Treat compliance as an operational lens that helps you enter markets with confidence.”
Supply Chain, Logistics, and Currency Strategy for New Markets
Supply chains must be mapped early so you know how products will reach customers and at what cost.
Customs, last-mile delivery, and local distribution choices
Partner with established local distributors to cut time-to-market and handle import procedures. They already know permits, lead times, and last-mile options in the target market.
Choose partners who match your product service standards and can manage returns, labeling, and local packaging rules.
Managing FX exposure and pricing tactics
Work with banking and FX partners to accept local currency and manage volatility. You can hedge, price in local currency, or set FX buffers to protect margins.
- You’ll evaluate customs requirements, lead times, and last-mile options so products services arrive reliably and fast.
- You’ll model landed costs end-to-end so pricing covers duties, freight, and support without surprising buyers.
- You’ll adapt packaging, labeling, and returns workflows for local markets to keep costs and experiences predictable.
- You’ll integrate logistics data into commercial planning so sales promises reflect real capacity and market conditions.
- You’ll pilot in a limited geography to validate SLAs and delivery quality before scaling the fulfillment network.
“Supply chain partners and smart FX planning turn market entry from a risk into a repeatable engine for growth.”
Sequencing Markets: Pick the Markets Right and in the Right Order
The order you enter markets can save capital, time, and reputation.
Start with a simple scoring model that ranks demand, competition, regulation, and operational fit. Use weighted criteria so you reliably pick the markets right for your business.
Agile testing with EOR before deeper investment
Use an EOR to hire fast and legally in a new market without forming an entity. That lets you validate demand and refine product-market fit before larger commitments.
Run a short market-first pilot, measure CAC/LTV, and make go/no-go calls at stage gates tied to clear KPIs.
Avoiding reactive expansion and copycat moves
Don’t rush because a competitor opened there. Conduct thorough market research tailored to your offer and operating model.
Learn from real missteps — like Target’s Canada launch — where speed beat validation and costs rose fast.
- Prioritize: score geographies on demand, competition, and market conditions.
- Test: run market first pilots with EORs, then scale if metrics justify deeper investment.
- Protect: define fallback actions — pivot, change pricing, or pause — when signals are weak.
- Align: sequence markets based on supply chain, data rules, and language dependencies.
“Pick markets in a deliberate order so each launch compounds learning and reduces risk.”
Measure, Learn, and Adapt: KPIs for Successful Global Expansion
Measure what matters so you can pivot fast when a market surprises you. Clear KPIs help you protect capital and grow your customer base in new markets.
Market entry milestones, CAC/LTV by region, and compliance health
Track simple milestones: entity or EOR setup, first hires, first deals, and payback periods. These milestones show real momentum and flag when to pause or push.
- Unit economics: break down CAC, LTV, and sales cycle by region to spot scalable markets.
- Compliance health: monitor filings, audits, and training as leading indicators to avoid surprises.
- Product metrics: measure product service adoption, NPS, and retention to confirm value.
- Brand & revenue: track brand recognition lift, share of voice, and revenue streams by country and currency.
- Reviews: run quarterly performance reviews to reallocate resources to high-performing markets and fix bottlenecks quickly.
“Use disciplined measurement to turn noisy launches into reliable learning.”
Conclusion
Wrap up with clear next steps so your work becomes action, not just notes. A concise plan ties objectives, research, entry model, and localization into one usable global expansion strategy.
Use partners and the right tools to lower complexity. Pick measurable KPIs and review them often so you can pivot fast when a market signals change.
You’ll leave ready to test, validate, and scale. With sequencing, compliance, and local hires in place, your company can start taking business into new markets and growing with confidence.
Ready to pilot a market? Start small, measure well, and let each success fund the next move around the world.